参考:https://medium.com/tech-tajawal/jwt-authentication-for-lumen-5-6-2376fd38d454
1.Add JWT_SECRET=xxxx to yours.env file
APP_KEY=1111
JWT_SECRET=1112. Create a migration file for the users table:
php artisan make:migration create_users_table3. Modify the migration file created inside the database/migrations directory
/**
* Run the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function up()
{
Schema::create('users', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->bigIncrements('id');
$table->string('name');
$table->string('email')->unique();
$table->timestamp('email_verified_at')->nullable();
$table->string('password');
$table->rememberToken();
$table->timestamps();
});
}4. create the seeder to populate the database with some users. Modify database/seeds/UsersTableSeeder.php to look like:
/**
* Run the database seeds.
*
* @return void
*/
public function run()
{
DB::table('users')->insertOrIgnore(
[
[
'name' => 'Admin',
'email' => '[email protected]',
'password' => Hash::make('password'),
],
[
'name' => 'Editor',
'email' => '[email protected]',
'password' => Hash::make('password'),
],
[
'name' => 'User',
'email' => '[email protected]',
'password' => Hash::make('password'),
]
]
);
}5. Now create the configured database in MySQL and run the following commands inside your terminal to create the users table and add some dummy data respectively:
php artisan migrate
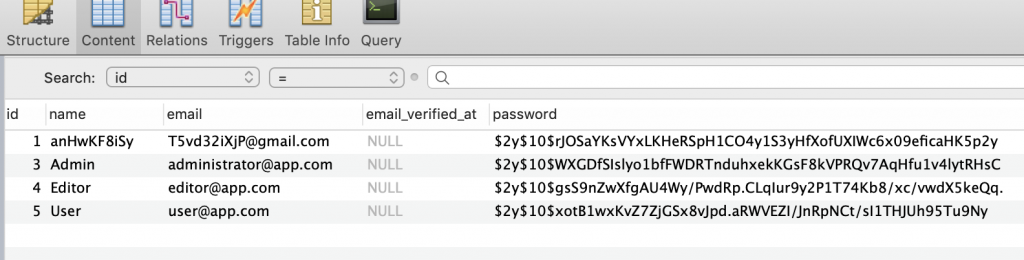
php artisan db:seedNow your database looks something like this:
6. Lumen does not have facades and eloquent enabled by default, let’s enable them first by opening the bootstrap/app.php file and uncomment the following lines:
$app->withFacades();
$app->withEloquent();7. Now let’s create the endpoint to generate JWT token. There are tons of libraries out there that will help you with it we will use the one called firebase/php-jwt. Open up your terminal and run the following command to pull it in using composer:
composer require firebase/php-jwt8. Now let’s add the endpoint POST /auth/v1/login that will accept the credentials and return a token for us. Let’s register the route first by adding the following route inside routes/web.php file:
$router->group(['prefix' => 'auth/v1'], function () use ($router) {
$router->post('login', 'AuthController@login');
});8. Now we need the controller AuthController with method authenticate. Inside app/Http/Controllers folder create a new AuthController.php file and put following content inside it:
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use Validator;
use App\User;
use Firebase\JWT\JWT;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use Firebase\JWT\ExpiredException;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Auth;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Hash;
class AuthController extends Controller
{
private $request;
/**
* Create a new AuthController instance.
*
* @return void
*/
public function __construct(Request $request)
{
$this->request = $request;
}
/**
* Get a JWT via given credentials.
*
* @return \Illuminate\Http\JsonResponse
*/
public function login(User $user)
{
$this->validate($this->request, [
'email' => 'required|email',
'password' => 'required'
]);
// Find the user by email
$user = User::where('email', $this->request->input('email'))->first();
if (!$user) {
// You wil probably have some sort of helpers or whatever
// to make sure that you have the same response format for
// differents kind of responses. But let's return the
// below respose for now.
return response()->json([
'error' => 'Email does not exist.'
], 400);
}
// Verify the password and generate the token
if (Hash::check($this->request->input('password'), $user->password)) {
return response()->json([
'token' => $this->jwt($user),
'token_type' => 'bearer',
'data' => $user
], 200);
}
// Bad Request response
return response()->json([
'error' => 'Email or password is wrong.'
], 400);
}
/**
* Get the authenticated User.
*
* @return \Illuminate\Http\JsonResponse
*/
public function me()
{
$user = Auth::user();
return response()->json($user);
}
/**
* Create a new token.
*
* @param \App\User $user
* @return string
*/
protected function jwt(User $user)
{
$payload = [
'iss' => "lumen-jwt", // Issuer of the token
'sub' => $user->id, // Subject of the token
'iat' => time(), // Time when JWT was issued.
'exp' => time() + 60 * 60 // Expiration time
];
// As you can see we are passing `JWT_SECRET` as the second parameter that will
// be used to decode the token in the future.
return JWT::encode($payload, env('JWT_SECRET'));
}
}
10. Let’s open up your terminal and then run the application by running the following command:
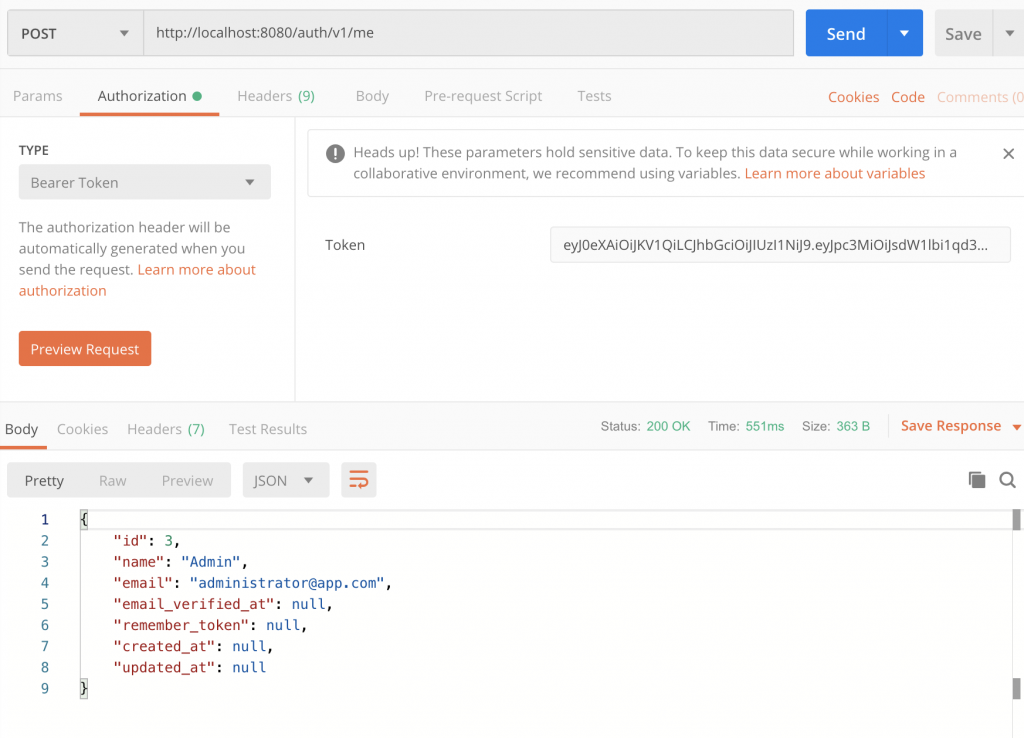
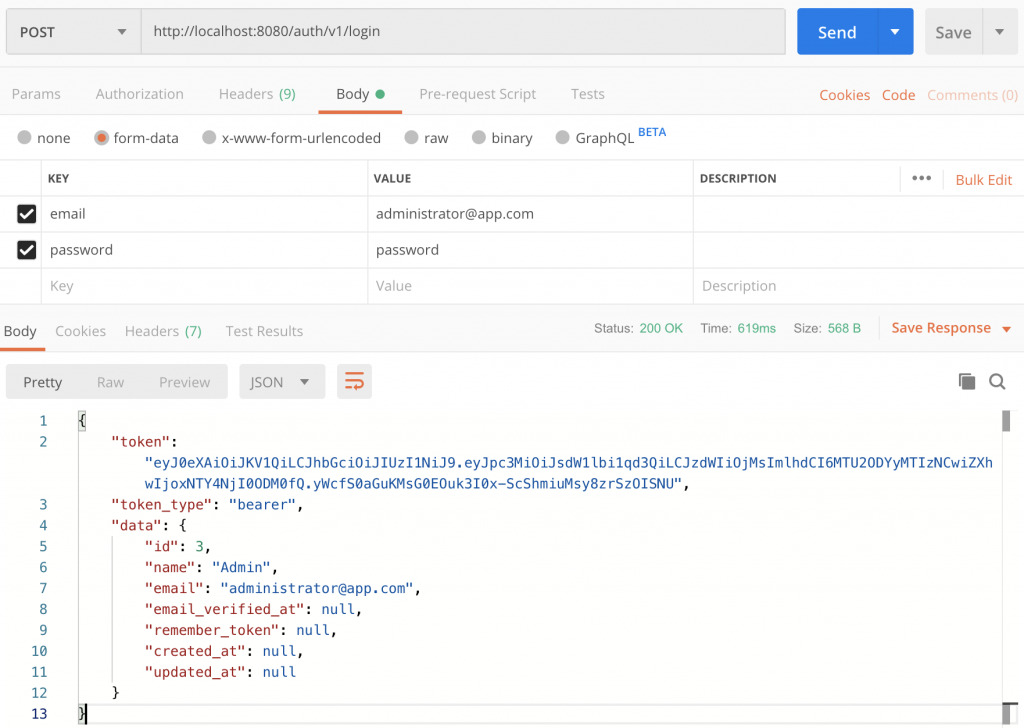
php -S localhost:8000 -t public11. Now to test our application i am using Postman. Inside postman create a new request to http://localhost:8000/auth/v1/login. When you hist this route by clicking the send button you will get the the token in response body.
12. Authentication
Uncomment lines in bootstrap/app.php
$app->routeMiddleware([
'auth' => App\Http\Middleware\Authenticate::class,
]);
......
$app->register(App\Providers\AuthServiceProvider::class);13. Now let’s protect some of our routes. Open the routes file i.e. routes/web.php and put the following routes inside it:
$router->group(['middleware' => 'auth'], function () use ($router) {
$router->group(['prefix' => 'auth/v1'], function () use ($router) {
$router->post('me', 'AuthController@me');
});
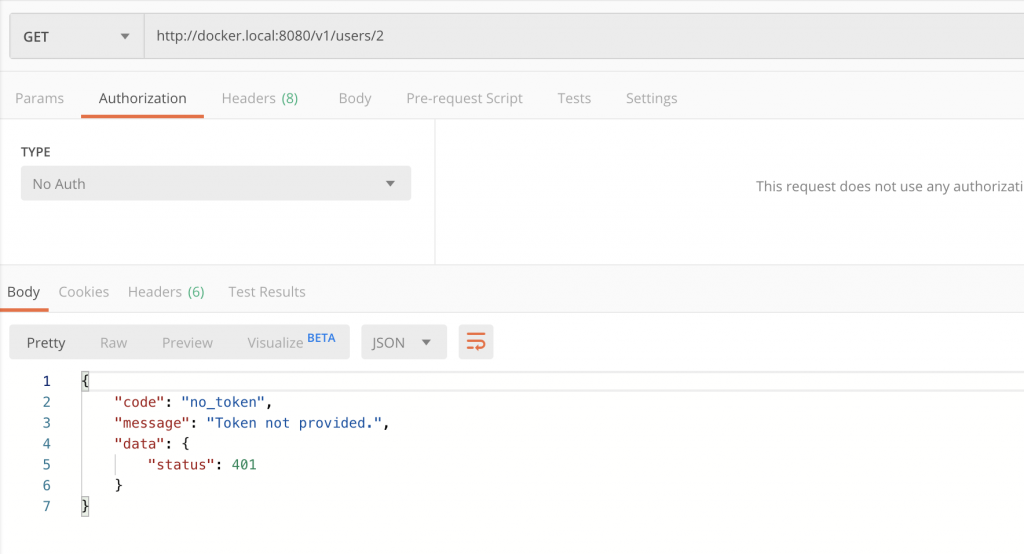
});14. After updating the routes file test if our request succeeds by hitting http://localhost:8000/auth/v1/me route. This request will fail because this is a protected route and require us to provide a token.
15. let’s edit App\HTTP\Middleware\Authenticate.php
<?php
namespace App\Http\Middleware;
use App\User;
use Closure;
use Exception;
use Firebase\JWT\JWT;
use Firebase\JWT\ExpiredException;
use Illuminate\Contracts\Auth\Factory as Auth;
class Authenticate
{
/**
* The authentication guard factory instance.
*
* @var \Illuminate\Contracts\Auth\Factory
*/
protected $auth;
/**
* Create a new middleware instance.
*
* @param \Illuminate\Contracts\Auth\Factory $auth
* @return void
*/
public function __construct(Auth $auth)
{
$this->auth = $auth;
}
/**
* Handle an incoming request.
*
* @param \Illuminate\Http\Request $request
* @param \Closure $next
* @param string|null $guard
* @return mixed
*/
public function handle($request, Closure $next, $guard = null)
{
// check dose token provided
$token = $request->header('authorization');
if (is_null($token)) {
// Unauthorized response if token not there
return response([
'code' => 'no_token',
'message' => 'Token not provided.',
'data' => [
'status' => 401
]
], 401);
}
// decode and check Token
$token = str_replace('Bearer ', '', $token);
try {
$token = str_replace('Bearer ', '', $token);
$credentials = JWT::decode($token, env('JWT_SECRET'), ['HS256']);
$user = User::find($credentials->sub);
if (!$user) {
return response([
'code' => 'user_not_found',
'message' => 'User not found',
'data' => [
'status' => 400,
]
], 400);
}
// Now let's put the user in the request class so that you can grab it from there
$request->auth = $user;
} catch (ExpiredException $e) {
return response([
'code' => 'token_expired',
'message' => 'Provided token is expired.',
'data' => [
'status' => 400,
]
], 400);
} catch (Exception $e) {
return response([
'code' => 'decode_token_failed',
'message' => 'An error while decoding token.',
'data' => [
'status' => 400,
]
], 400);
}
return $next($request);
}
}在之前的 Middleware 里,我们一句吧 token 里的 ID 获取到的 User 对象传递到 $request 里,现在到APP\Providers\AuthServiceProvider.php ,修改 boot() 为:
<?php
namespace App\Providers;
use Illuminate\Support\ServiceProvider;
class AuthServiceProvider extends ServiceProvider
{
/**
* Register any application services.
*
* @return void
*/
public function register()
{
//
}
/**
* Boot the authentication services for the application.
*
* @return void
*/
public function boot()
{
$this->app['auth']->viaRequest('api', function ($request) {
// recive current user object from middleware
if ($request->auth) {
return $request->auth;
}
});
}
}这样就可以通过 Auth::user() 获取当前用户信息。
16. make a request /auth/v2/me again: